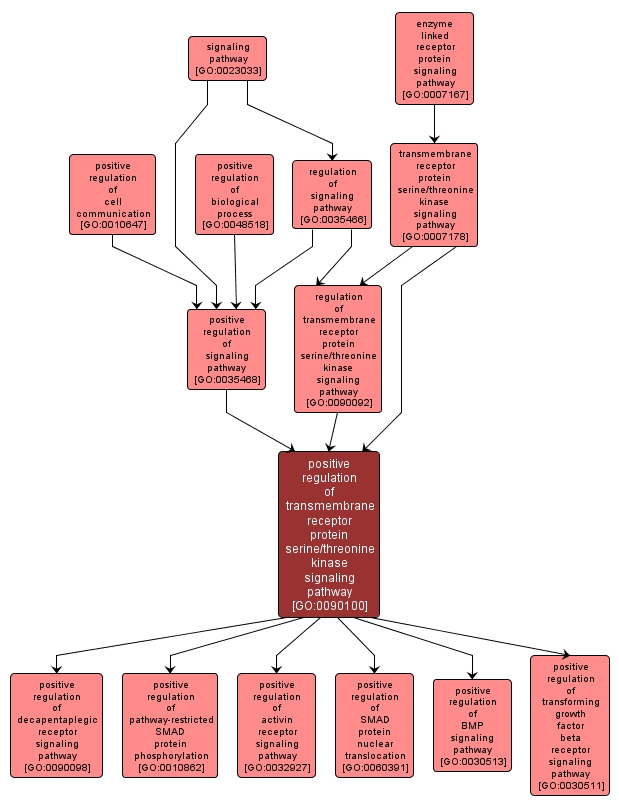
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
positive regulation of transmembrane receptor protein serine/threonine kinase signaling pathway |
| Acc: |
GO:0090100 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Any process that increases the rate, frequency, or extent of the series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a transmembrane receptor serine/threonine kinase binding to its physiological ligand. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|