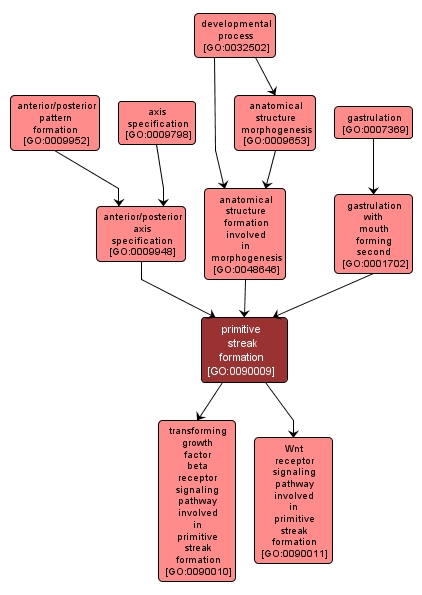
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
primitive streak formation |
| Acc: |
GO:0090009 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The developmental process pertaining to the initial formation of the primitive streak from unspecified parts. The primitive streak is a ridge of cells running along the midline of the embryo where the mesoderm ingresses. It defines the anterior-posterior axis. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|