| Desc: |
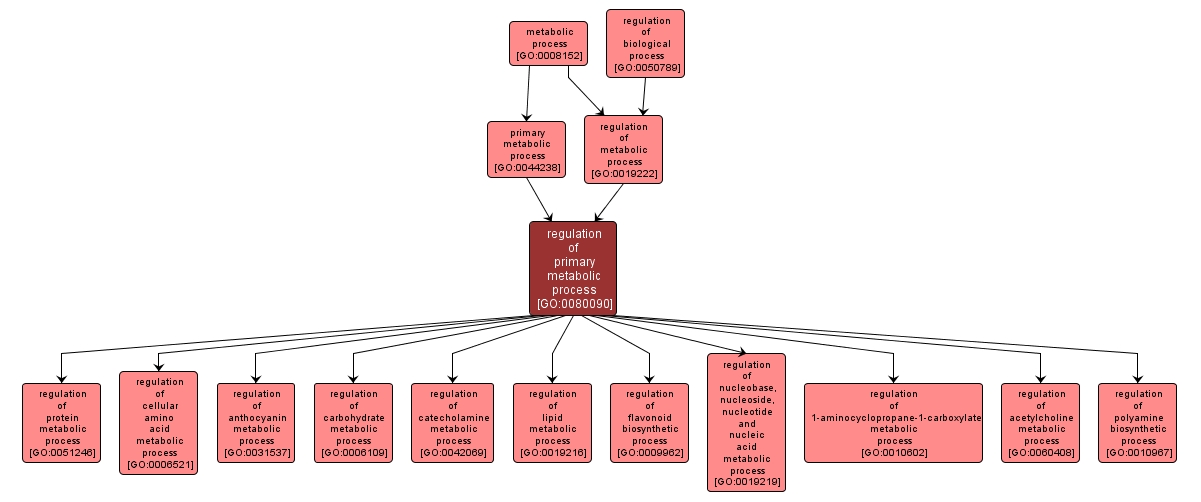
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways within a cell or an organism involving those compounds formed as a part of the normal anabolic and catabolic processes. These processes take place in most, if not all, cells of the organism. |