| Desc: |
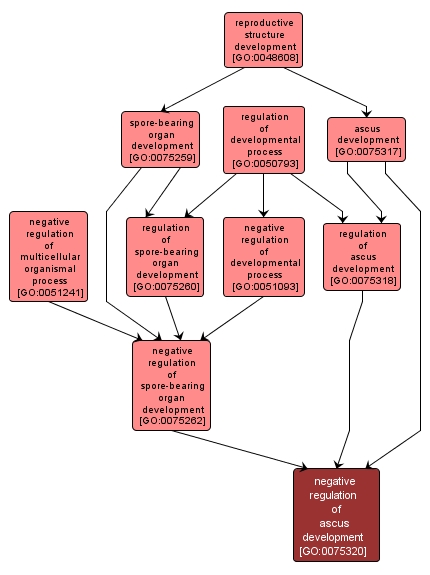
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of ascus development, a saclike structure produced by fungi of the phylum Ascomycota (sac fungi) in which sexually produced spores (ascospores), usually four or eight in number, are formed. |