| Desc: |
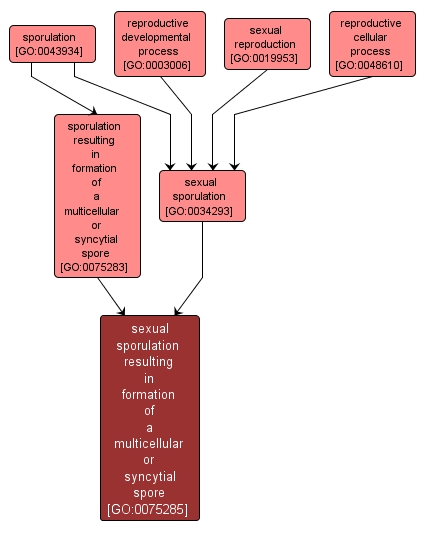
The formation of multicellular or syncytial spore via septations derived from meiosis. A multicellular or syncytial spore is a structure that can be used for dissemination, for survival of adverse conditions because of its heat and dessication resistance, and/or for reproduction. |