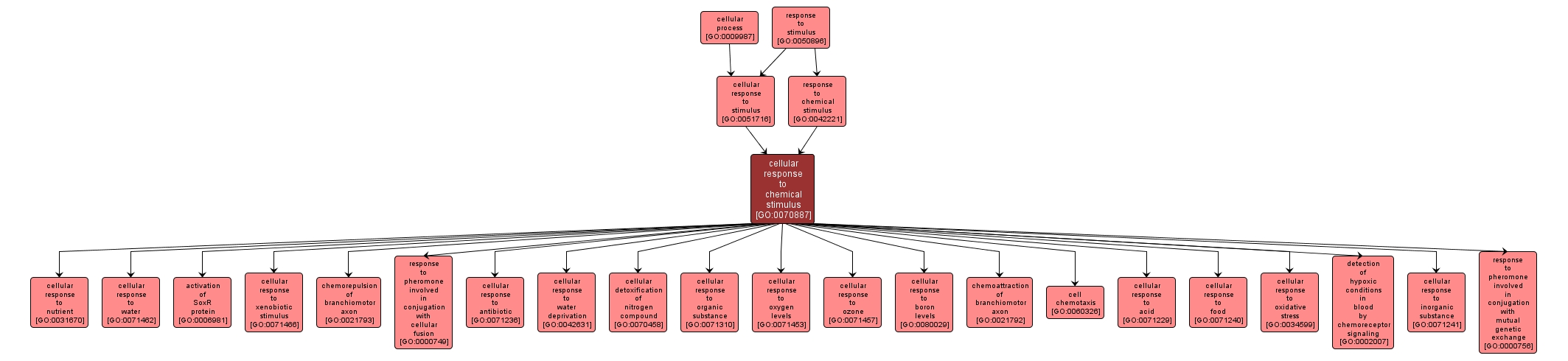
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
cellular response to chemical stimulus |
| Acc: |
GO:0070887 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
A change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a chemical stimulus. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|