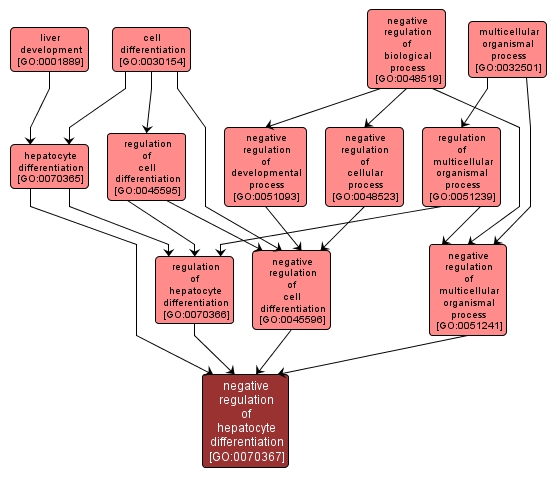
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
negative regulation of hepatocyte differentiation |
| Acc: |
GO:0070367 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Any process that stops or decreases the rate or extent of hepatocyte differentiation. |
Synonyms:
- down-regulation of hepatocyte differentiation
- down regulation of hepatocyte differentiation
- downregulation of hepatocyte differentiation
- inhibition of hepatocyte differentiation
- negative regulation of liver cell differentiation
|