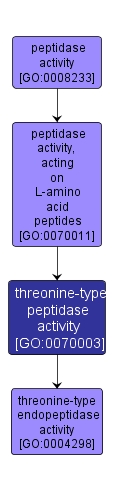
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
threonine-type peptidase activity |
| Acc: |
GO:0070003 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of peptide bonds in a polypeptide chain by a mechanism in which the hydroxyl group of a threonine residue at the active center acts as a nucleophile. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|