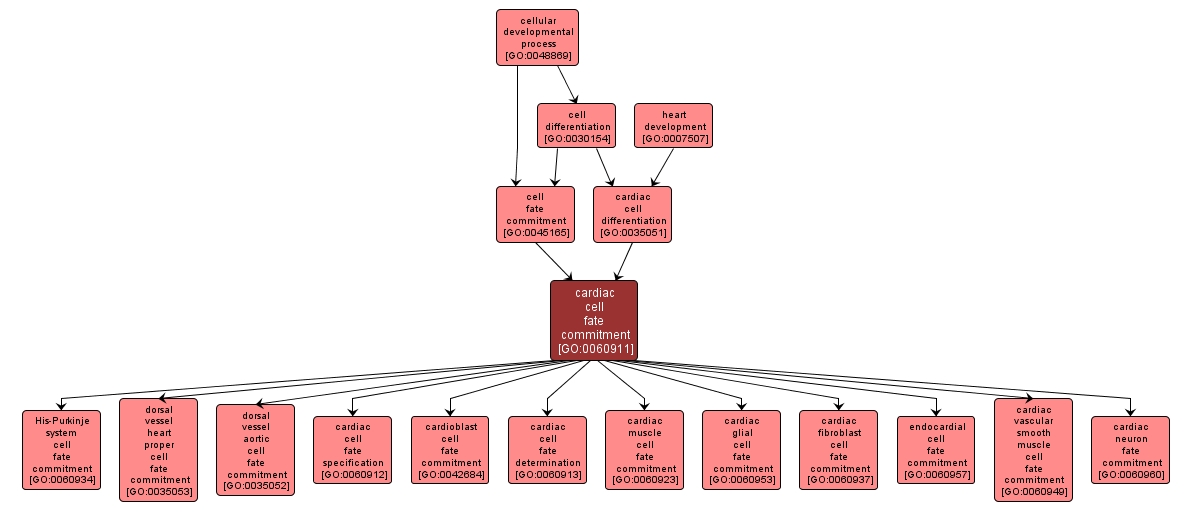
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
cardiac cell fate commitment |
| Acc: |
GO:0060911 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The commitment of cells to specific cardiac cell fates and their capacity to differentiate into cardiac cells. Cardiac cells are cells that comprise the organ which pumps blood through the circulatory system. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|