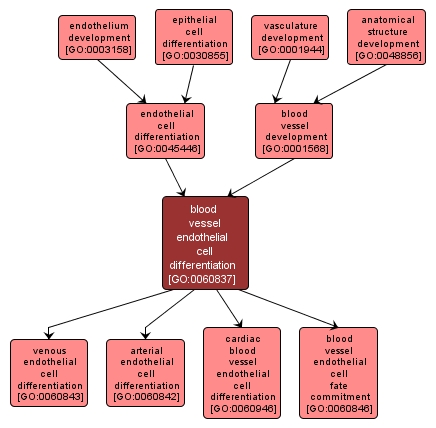
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
blood vessel endothelial cell differentiation |
| Acc: |
GO:0060837 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a blood vessel endothelial cell, a thin flattened cell that lines the inside surfaces of blood vessels. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|