GO TERM SUMMARY
|
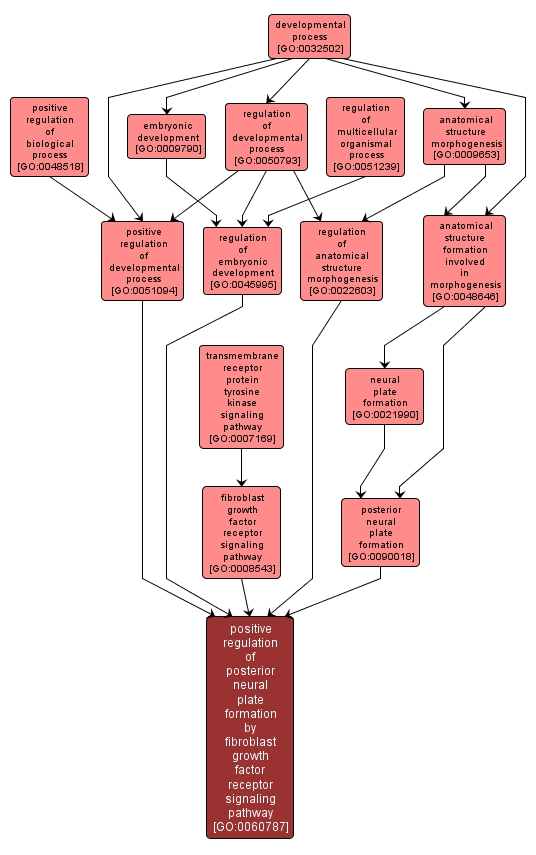
| Name: |
positive regulation of posterior neural plate formation by fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway |
| Acc: |
GO:0060787 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Any process that increases the rate or extent of the formation of the posterior neural plate, the posterior end of the flat, thickened layer of ectodermal cells known as the neural plate. |
Synonyms:
- positive regulation of posterior neural plate formation by FGF receptor signaling pathway
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|