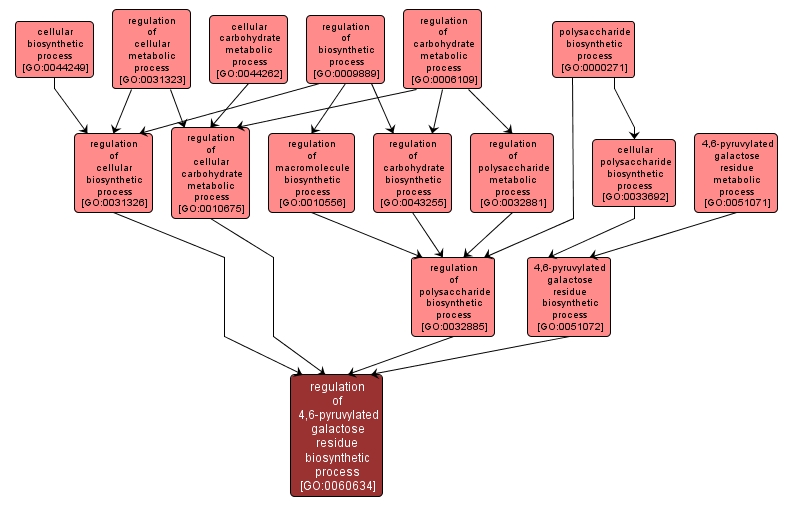
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
regulation of 4,6-pyruvylated galactose residue biosynthetic process |
| Acc: |
GO:0060634 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency, or extent of 4,6-pyruvylated galactose residue biosynthetic process, the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of the pyruvylated galactose residue 4-6-O-[(R)(1-carboxyethylidine)]-Gal-beta-1,3-. The galactose residue is part of a larger polysaccharide chain. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|