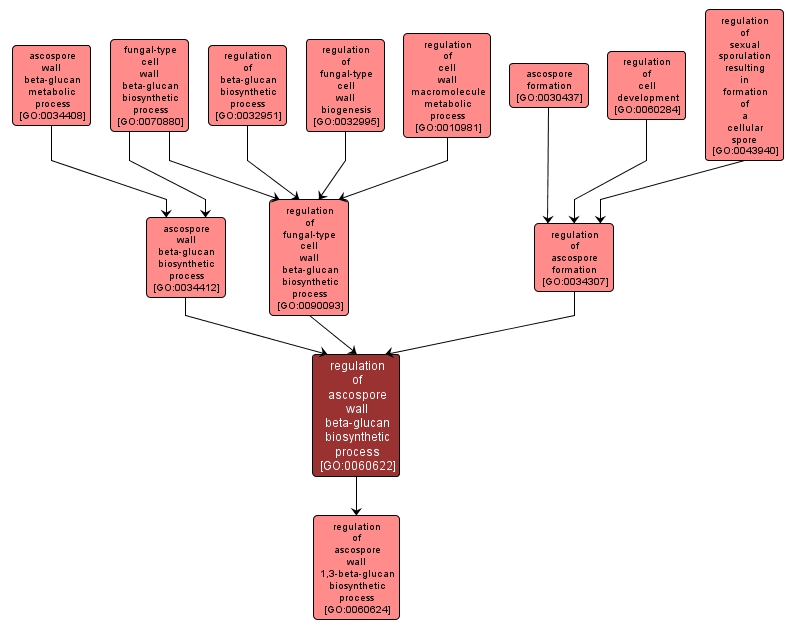
| Desc: |
Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of ascospore wall beta-glucan biosynthetic process, the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of beta-glucans, compounds composed of glucose residues linked by beta-D-glucosidic bonds, found in the walls of ascospores. |