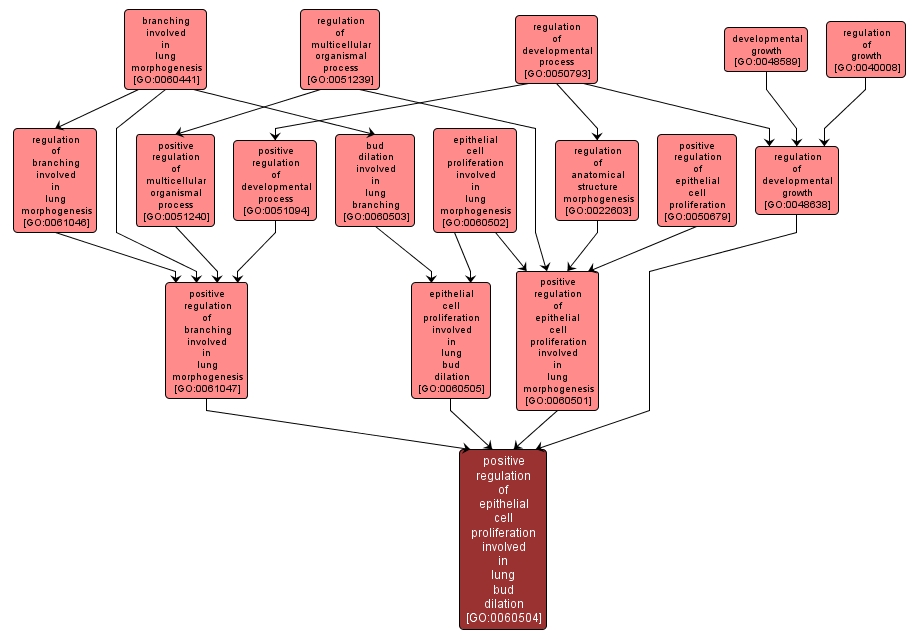
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation involved in lung bud dilation |
| Acc: |
GO:0060504 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Any process that increases the rate or frequency of epithelial cell proliferation that results in the lung bud increasing in size radially. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|