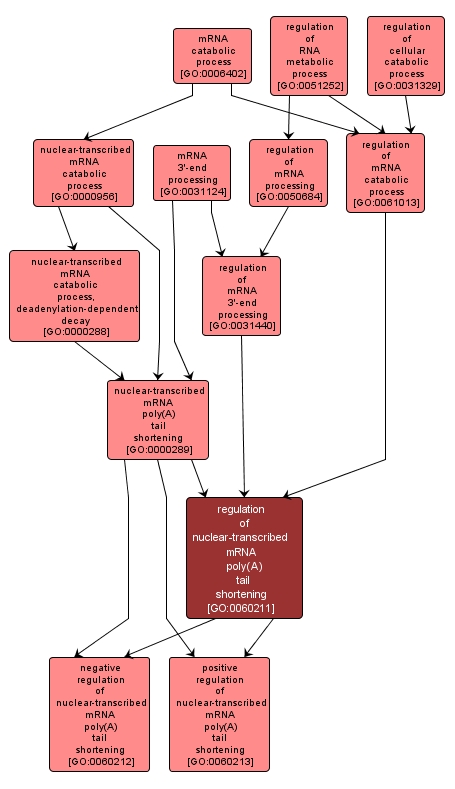
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
regulation of nuclear-transcribed mRNA poly(A) tail shortening |
| Acc: |
GO:0060211 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of poly(A) tail shortening of a nuclear-transcribed mRNA. Poly(A) tail shortening is the decrease in length of the poly(A) tail of an mRNA from full length to an oligo(A) length. |
Synonyms:
- regulation of nuclear mRNA poly(A) tail shortening
- regulation of 3' to 5' mRNA deadenylation
- regulation of mRNA deadenylation
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|