GO TERM SUMMARY
|
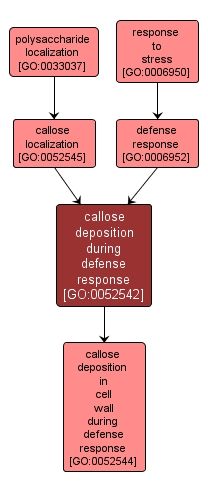
| Name: |
callose deposition during defense response |
| Acc: |
GO:0052542 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Any process by which callose is transported to, and/or maintained in, a specific location during the defense response. Callose is a linear 1,3-beta-d-glucan formed from UDP-glucose and is found in certain plant cell walls. |
Synonyms:
- callose localization during defense response
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|