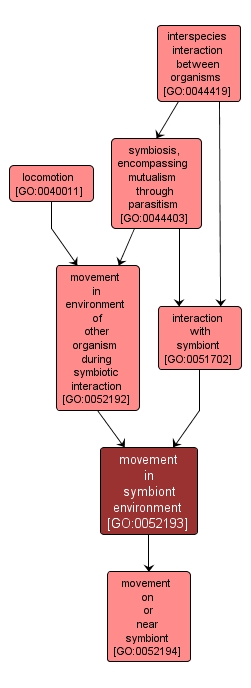
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
movement in symbiont environment |
| Acc: |
GO:0052193 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The directed movement of an organism or motile cell on, within or near its symbiont organism. The symbiont is defined as the smaller of the organisms involved in a symbiotic interaction. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|