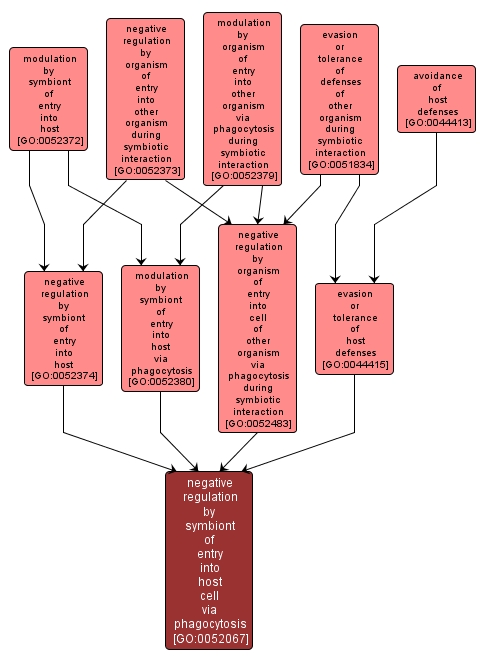
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
negative regulation by symbiont of entry into host cell via phagocytosis |
| Acc: |
GO:0052067 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Any process by which an organism stops or prevents itself undergoing phagocytosis into a cell in the host organism. The host is defined as the larger of the organisms involved in a symbiotic interaction. |
Synonyms:
- inhibition by symbiont of entry into host cell via phagocytosis
- negative regulation by organism of entry into host cell via host phagocytosis
- down regulation by symbiont of entry into host cell via phagocytosis
- down-regulation by symbiont of entry into host cell via phagocytosis
- downregulation by symbiont of entry into host cell via phagocytosis
|