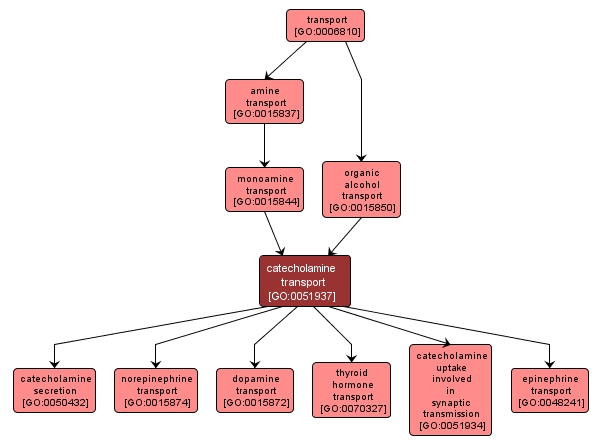
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
catecholamine transport |
| Acc: |
GO:0051937 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The directed movement of catecholamines, a group of physiologically important biogenic amines that possess a catechol (3,4-dihydroxyphenyl) nucleus and are derivatives of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylethylamine. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|