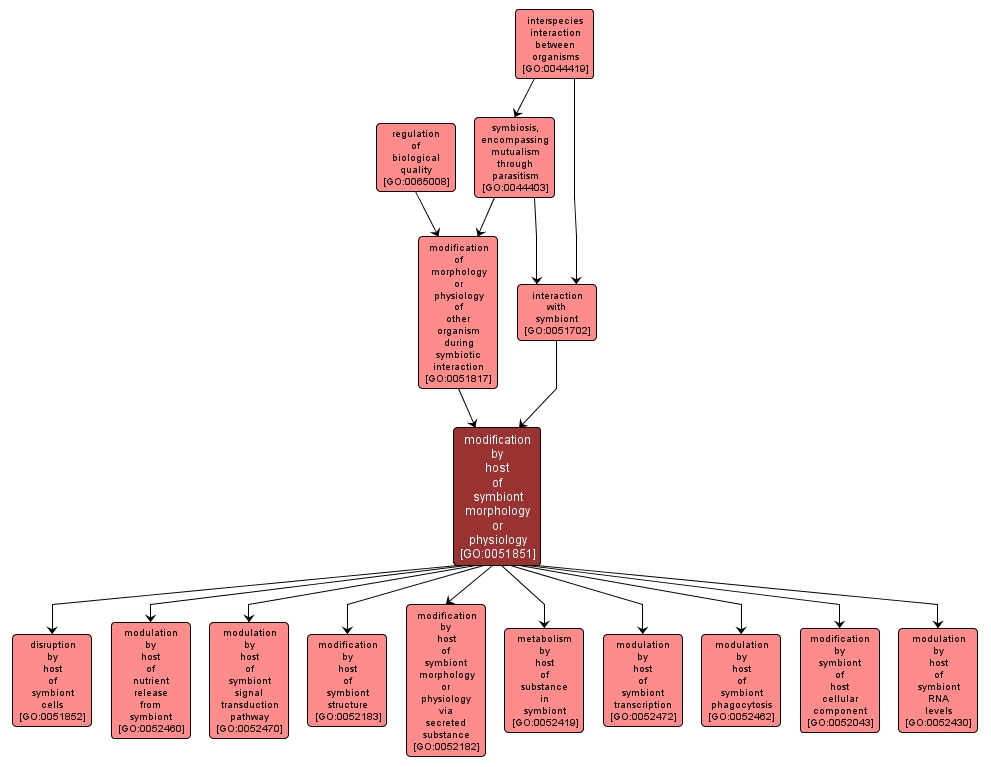
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
modification by host of symbiont morphology or physiology |
| Acc: |
GO:0051851 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The process by which an organism effects a change in the structure or processes of a symbiont organism. The symbiont is defined as the smaller of the organisms involved in a symbiotic interaction. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|