GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
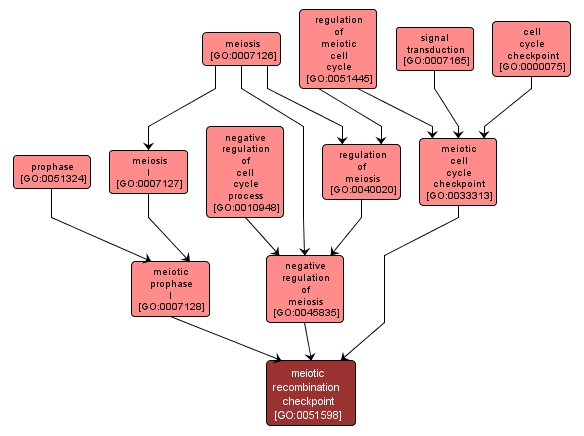
meiotic recombination checkpoint |
| Acc: |
GO:0051598 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
A checkpoint during late prophase I (pachytene) which prevents segregation of homologous chromosomes until recombination is completed and ensures proper distribution of the genetic material to the gametes. |
| Synonyms:
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|