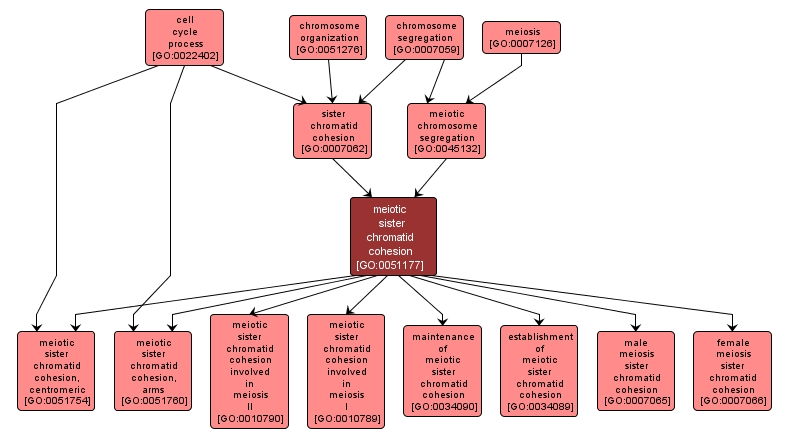
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
meiotic sister chromatid cohesion |
| Acc: |
GO:0051177 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The cell cycle process whereby sister chromatids of a replicated chromosome are joined along the entire length of the chromosome during meiosis. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|