GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
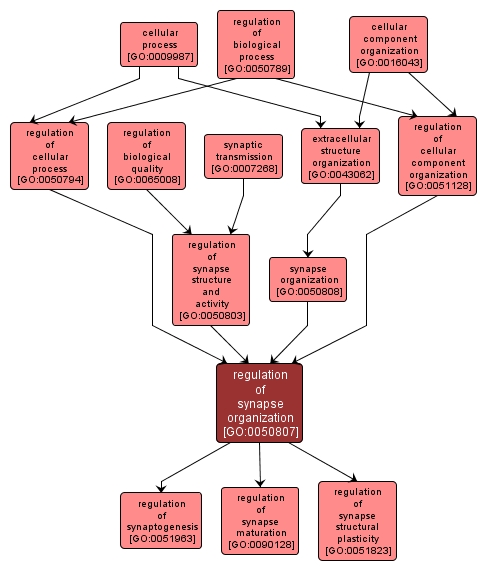
regulation of synapse organization |
| Acc: |
GO:0050807 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Any process that modulates the physical form of a synapse, the junction between a neuron and a target (neuron, muscle, or secretory cell). |
Synonyms:
- regulation of synapse organization and biogenesis
- regulation of synapse structure
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|