GO TERM SUMMARY
|
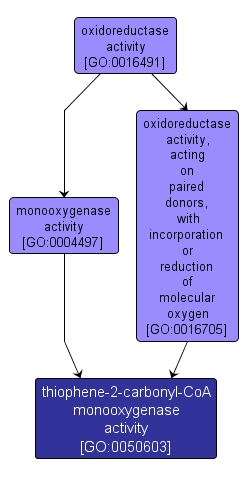
| Name: |
thiophene-2-carbonyl-CoA monooxygenase activity |
| Acc: |
GO:0050603 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Catalysis of the reaction: thiophene-2-carbonyl-CoA + AH2 + O2 = 5-hydroxythiophene-2-carbonyl-CoA + A + H2O. |
Synonyms:
- thiophene-2-carbonyl-CoA, hydrogen-donor:oxygen oxidoreductase activity
- thiophene-2-carboxyl-CoA hydroxylase activity
- thiophene-2-carboxyl-CoA monooxygenase activity
- thiophene-2-carboxyl-CoA dehydrogenase activity
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|