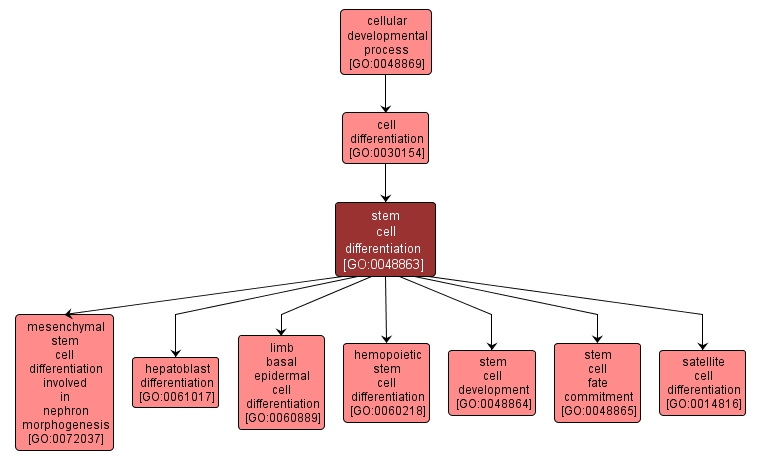
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
stem cell differentiation |
| Acc: |
GO:0048863 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The process whereby a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a stem cell. A stem cell is a cell that retains the ability to divide and proliferate throughout life to provide progenitor cells that can differentiate into specialized cells. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|