GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
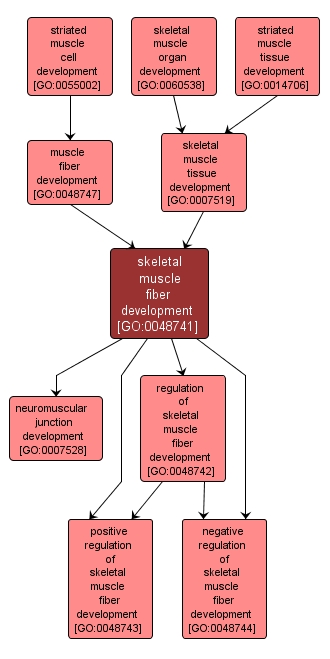
skeletal muscle fiber development |
| Acc: |
GO:0048741 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the skeletal muscle fiber over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Muscle fibers are formed by the maturation of myotubes. They can be classed as slow, intermediate/fast or fast. |
Synonyms:
- skeletal myofiber development
- skeletal muscle fibre development
- skeletal myofibre development
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|