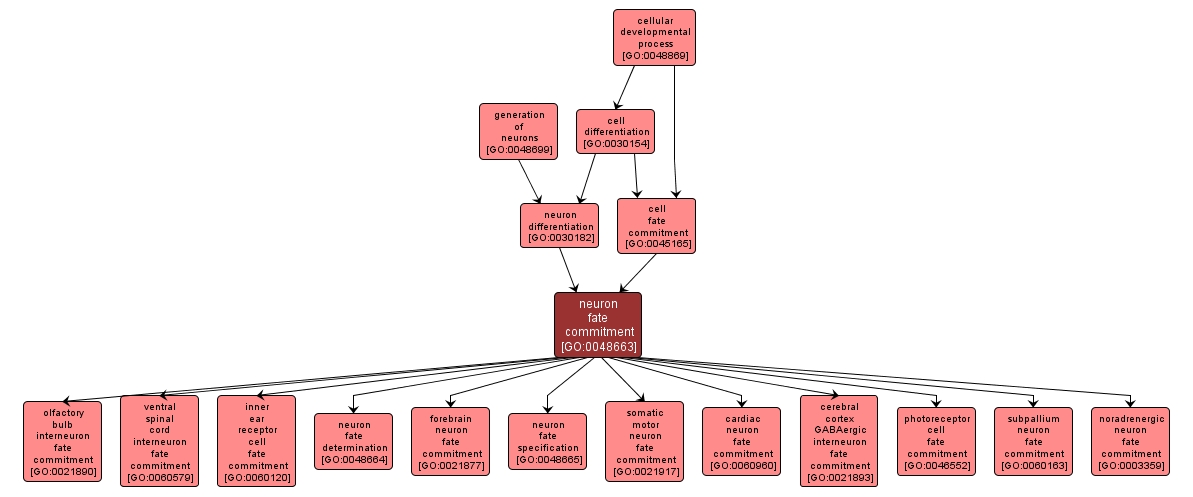
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
neuron fate commitment |
| Acc: |
GO:0048663 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The process whereby the developmental fate of a cell becomes restricted such that it will develop into a neuron. |
Synonyms:
- neuronal lineage restriction
- GO:0042055
- neuron lineage restriction
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|