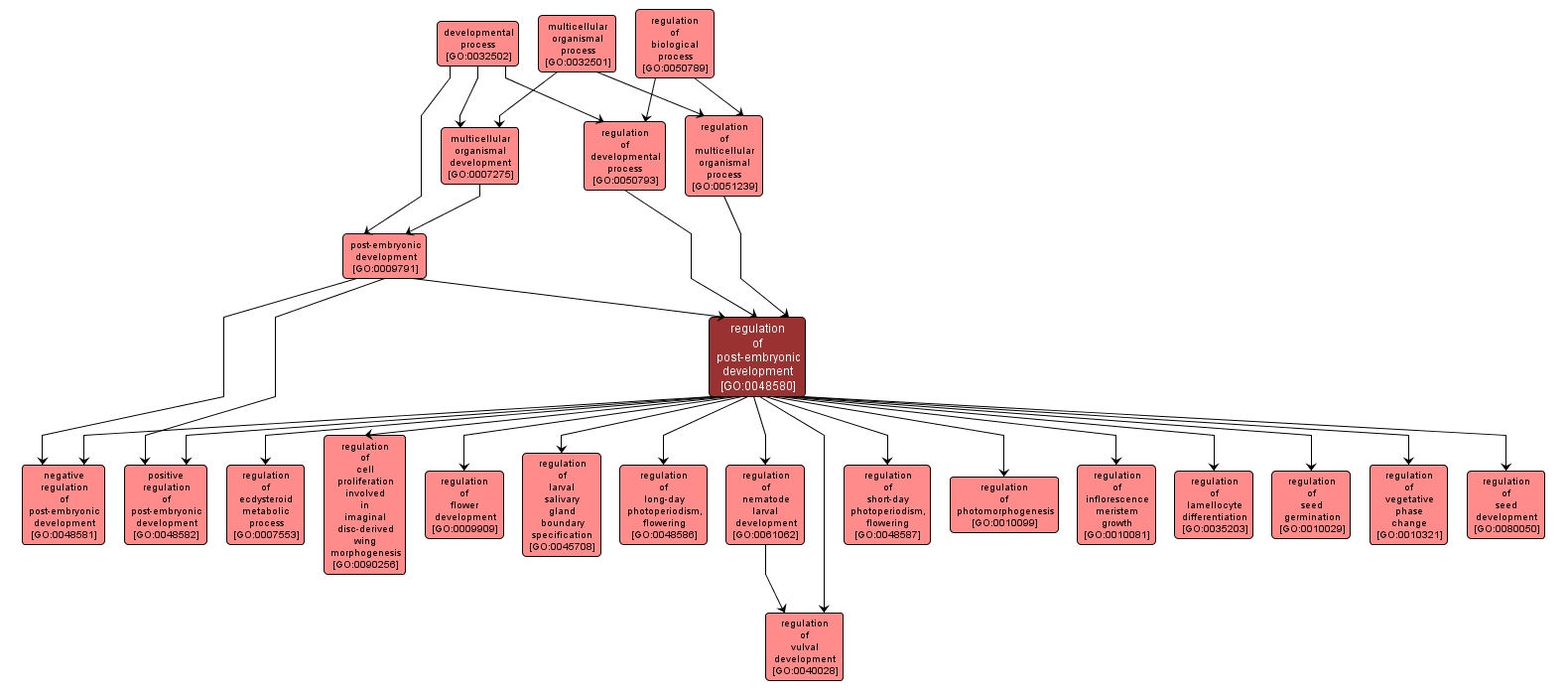
| Desc: |
Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of post-embryonic development. Post-embryonic development is defined as the process whose specific outcome is the progression of the organism over time, from the completion of embryonic development to the mature structure. |