| Desc: |
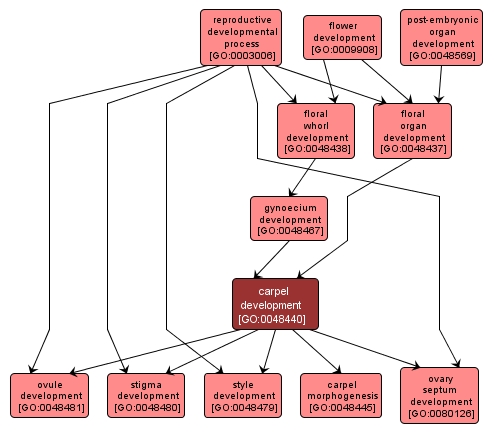
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the carpel over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A carpel is an organ (generally believed to be a modified foliar unit) at the centre of a flower, bearing one or more ovules and having its margins fused together or with other carpels to enclose the ovule in an ovary, and consisting also of a stigma and usually a style. |