| Desc: |
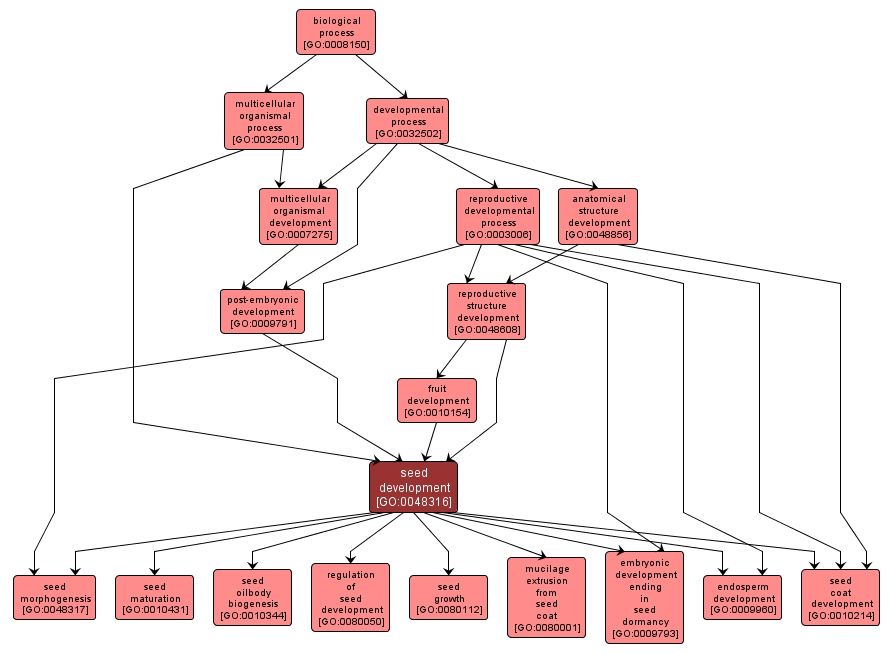
The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the seed over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A seed is a propagating organ formed in the sexual reproductive cycle of gymnosperms and angiosperms, consisting of a protective coat enclosing an embryo and food reserves. |