GO TERM SUMMARY
|
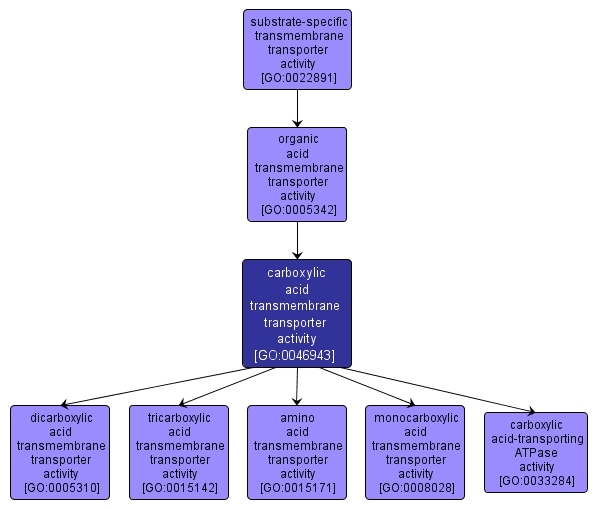
| Name: |
carboxylic acid transmembrane transporter activity |
| Acc: |
GO:0046943 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Catalysis of the transfer of carboxylic acids from one side of the membrane to the other. Carboxylic acids are organic acids containing one or more carboxyl (COOH) groups or anions (COO-). |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|