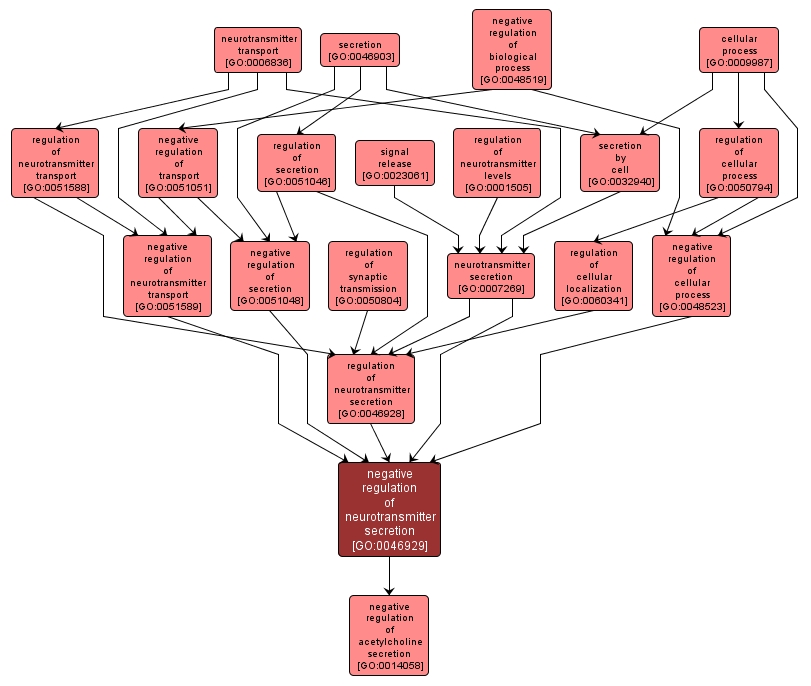
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
negative regulation of neurotransmitter secretion |
| Acc: |
GO:0046929 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of a neurotransmitter. |
Synonyms:
- down-regulation of neurotransmitter secretion
- down regulation of neurotransmitter secretion
- downregulation of neurotransmitter secretion
- conotoxin activity
- inhibition of neurotransmitter secretion
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|