GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
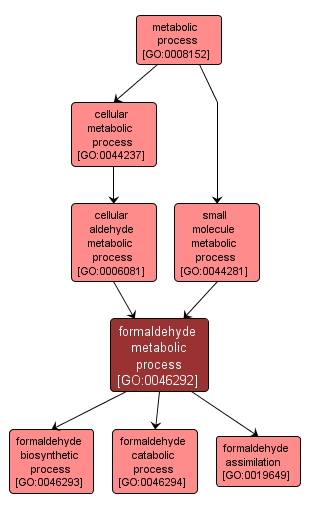
formaldehyde metabolic process |
| Acc: |
GO:0046292 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The chemical reactions and pathways involving formaldehyde (methanal, H2C=O), a colorless liquid or gas with a pungent odor, commonly used as a fixative or an antibacterial agent. |
Synonyms:
- methanal metabolism
- methanal metabolic process
- formaldehyde metabolism
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|