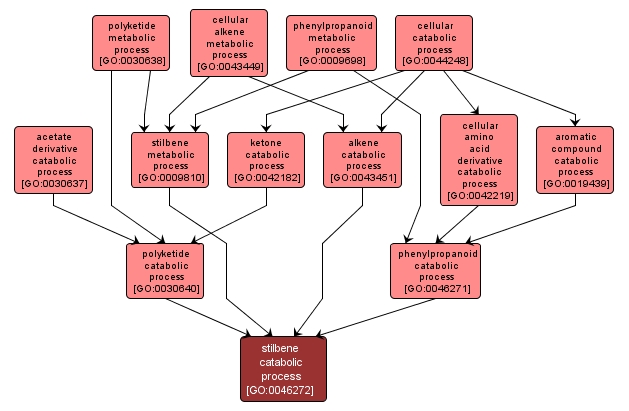
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
stilbene catabolic process |
| Acc: |
GO:0046272 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of stilbenes, a class of polyketide compounds formed from cinnamic acid and three molecules of malonyl CoA. |
Synonyms:
- stilbene catabolism
- stilbene degradation
- stilbene breakdown
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|