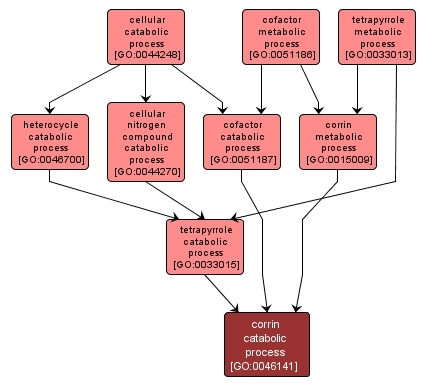
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
corrin catabolic process |
| Acc: |
GO:0046141 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of corrin, C19H22N4, the fundamental heterocyclic skeleton of the corrinoids. It consists of four reduced pyrrole rings joined into a macrocyclic ring. Corrin is the core of the vitamin B12 molecule. |
Synonyms:
- corrin degradation
- corrin catabolism
- corrin breakdown
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|