| Desc: |
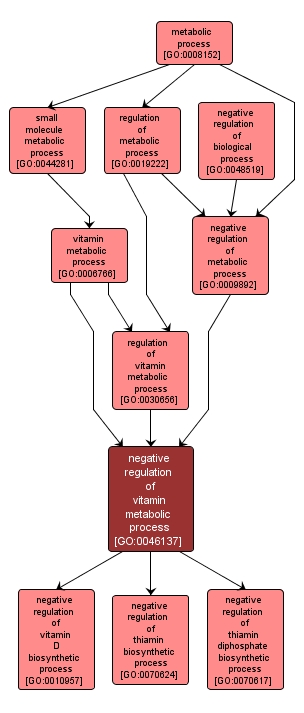
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a vitamin, one of a number of unrelated organic substances that occur in many foods in small amounts and that are necessary in trace amounts for the normal metabolic functioning of the body. |