| Desc: |
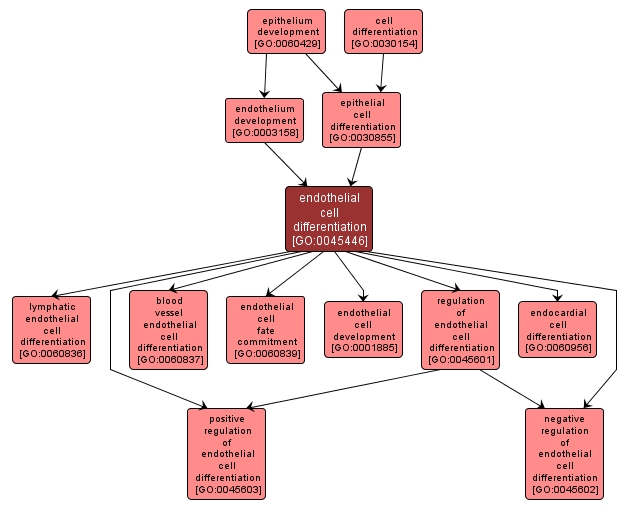
The process whereby a mesodermal angioblast acquires specialized features of an endothelial cell, a thin flattened cell. A layer of such cells lines the inside surfaces of body cavities, blood vessels, and lymph vessels, making up the endothelium. |