GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
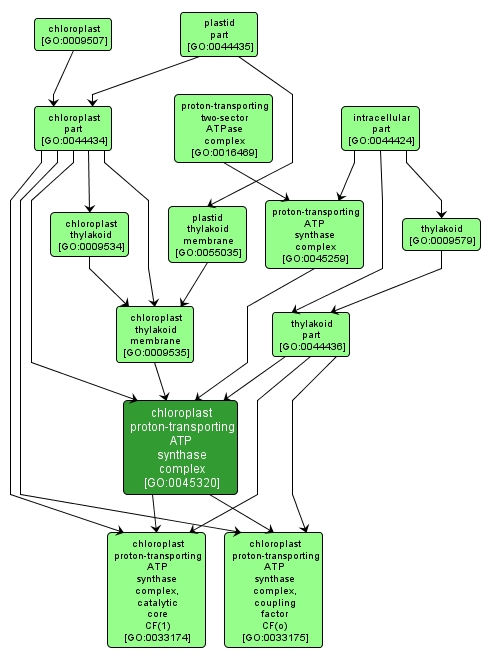
chloroplast proton-transporting ATP synthase complex |
| Acc: |
GO:0045320 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
A proton-transporting ATP synthase complex found in the chloroplast thylakoid membrane; it catalyzes the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP during photo-phosphorylation. |
Synonyms:
- chloroplast hydrogen-translocating F-type ATPase complex
- chloroplast proton-transporting F-type ATPase complex
- hydrogen-translocating F-type ATPase complex
|