GO TERM SUMMARY
|
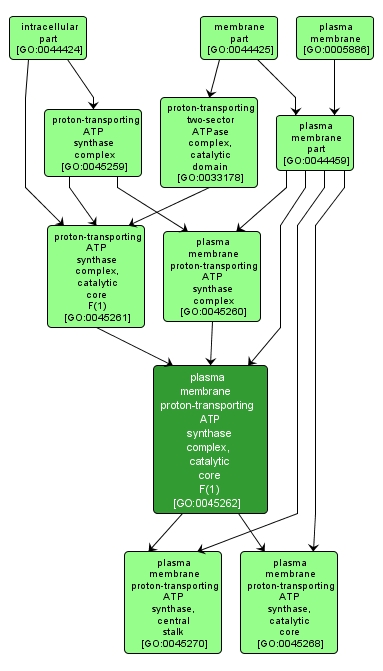
| Name: |
plasma membrane proton-transporting ATP synthase complex, catalytic core F(1) |
| Acc: |
GO:0045262 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
The catalytic sector of the plasma membrane hydrogen-transporting ATP synthase; it comprises the catalytic core and central stalk, and is peripherally associated with the plasma membrane when the entire ATP synthase is assembled. Examples of this component are found in Bacterial species. |
Synonyms:
- hydrogen-transporting ATP synthase, F1 sector
- proton-transporting ATP synthase complex, catalytic core F(1)
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|