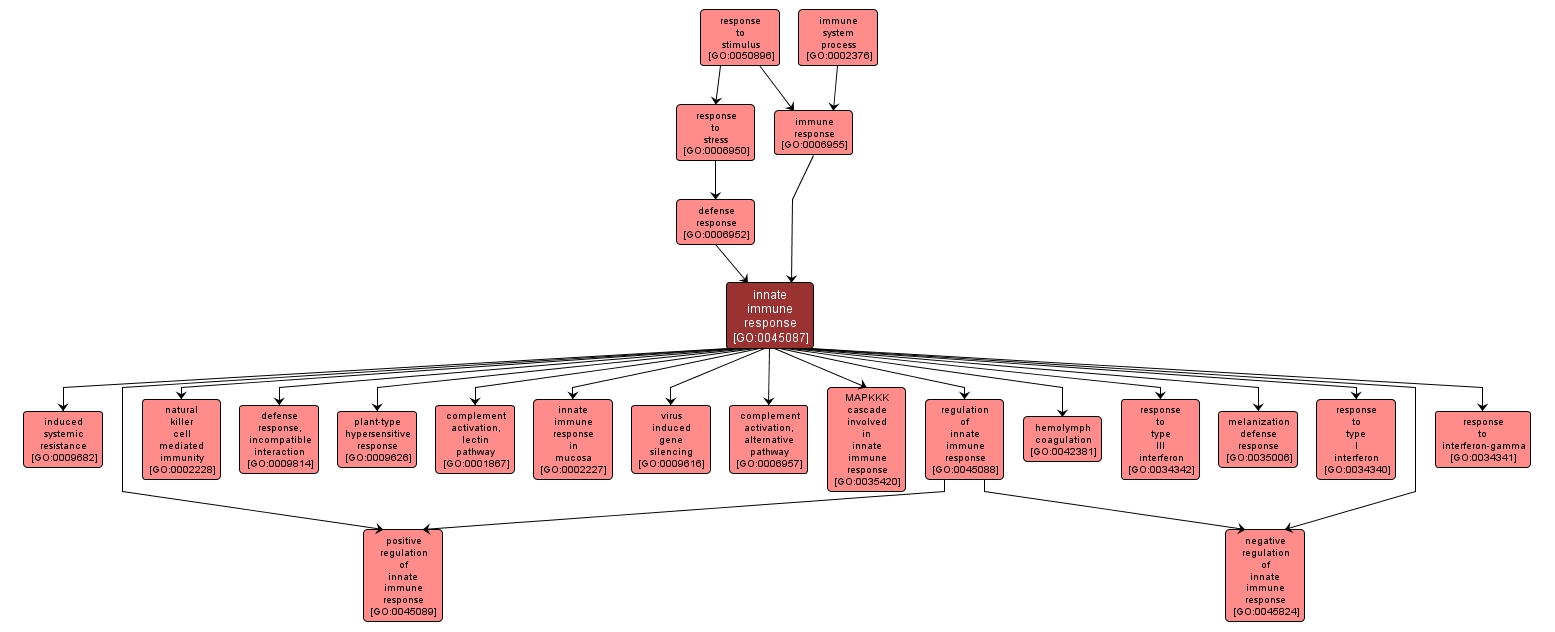
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
innate immune response |
| Acc: |
GO:0045087 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens. |
Synonyms:
- GO:0002226
- nonspecific immune response
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|