GO TERM SUMMARY
|
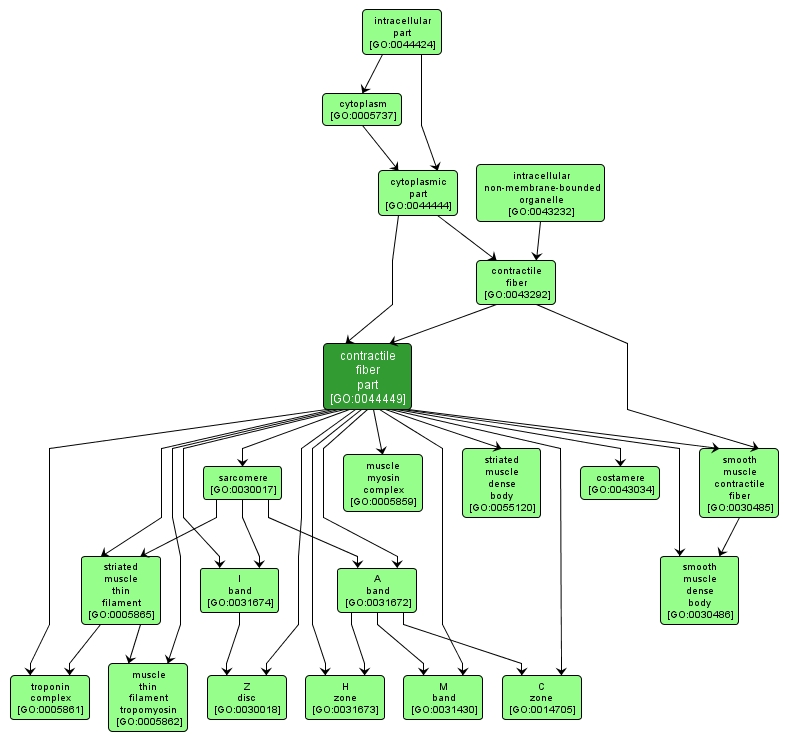
| Name: |
contractile fiber part |
| Acc: |
GO:0044449 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
Any constituent part of a contractile fiber, a fiber composed of actin, myosin, and associated proteins, found in cells of smooth or striated muscle. |
Synonyms:
- contractile fibre component
- muscle fiber component
- muscle fibre component
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|