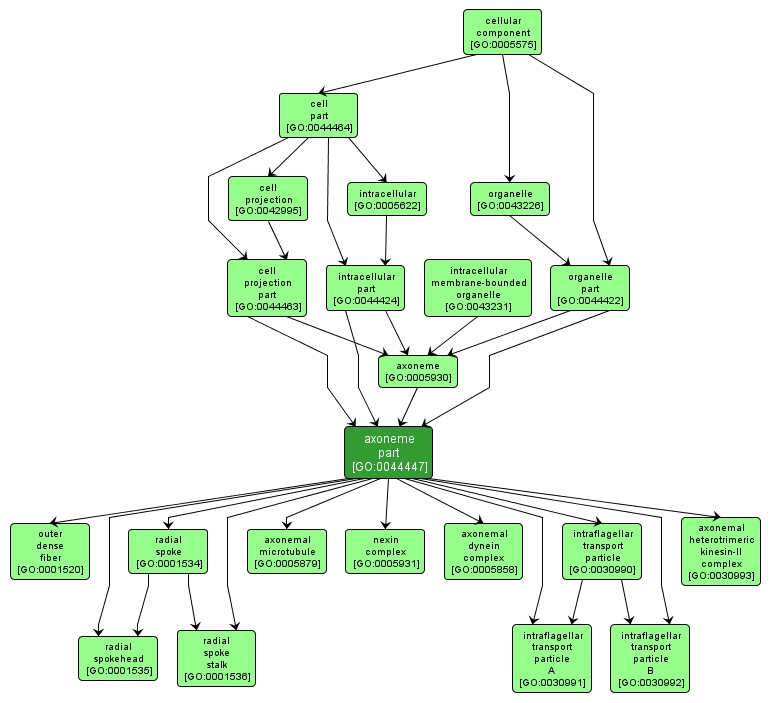
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
axoneme part |
| Acc: |
GO:0044447 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
Any constituent part of an axoneme, the bundle of microtubules and associated proteins that forms the core of cilia and flagella in eukaryotic cells and is responsible for their movements. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|