| Desc: |
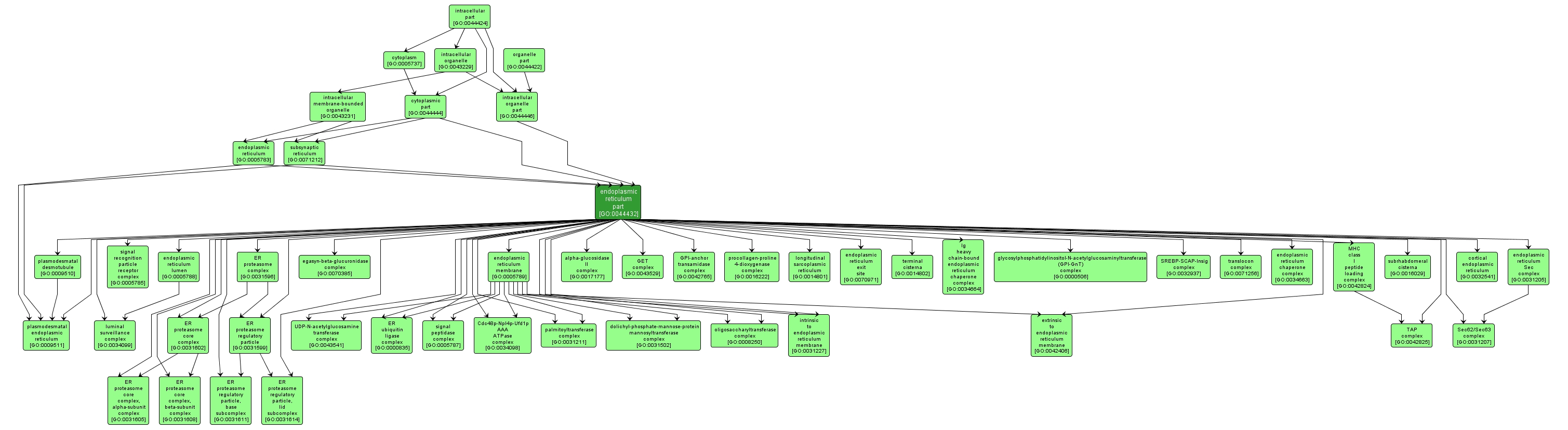
Any constituent part of the endoplasmic reticulum, the irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae. |