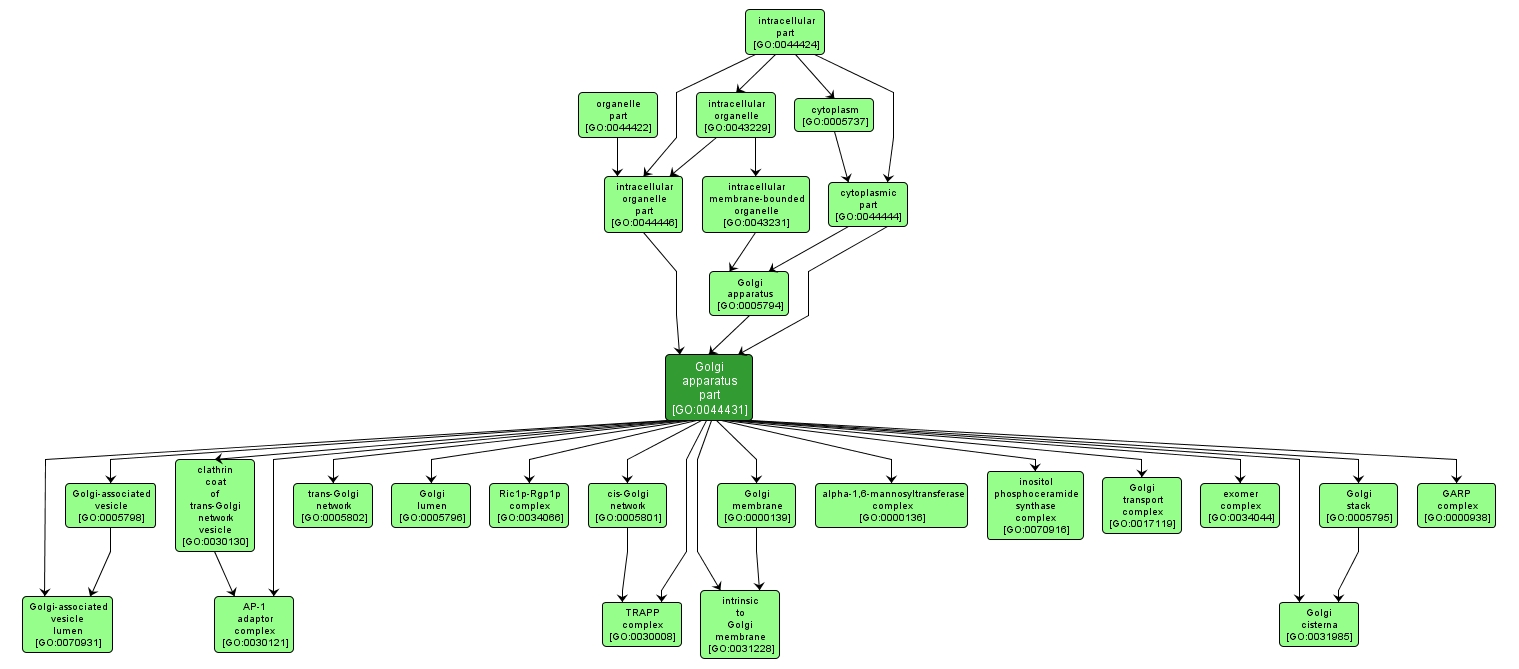
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
Golgi apparatus part |
| Acc: |
GO:0044431 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
Any constituent part of the Golgi apparatus, a compound membranous cytoplasmic organelle of eukaryotic cells, consisting of flattened, ribosome-free vesicles arranged in a more or less regular stack. |
| Synonyms:
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|