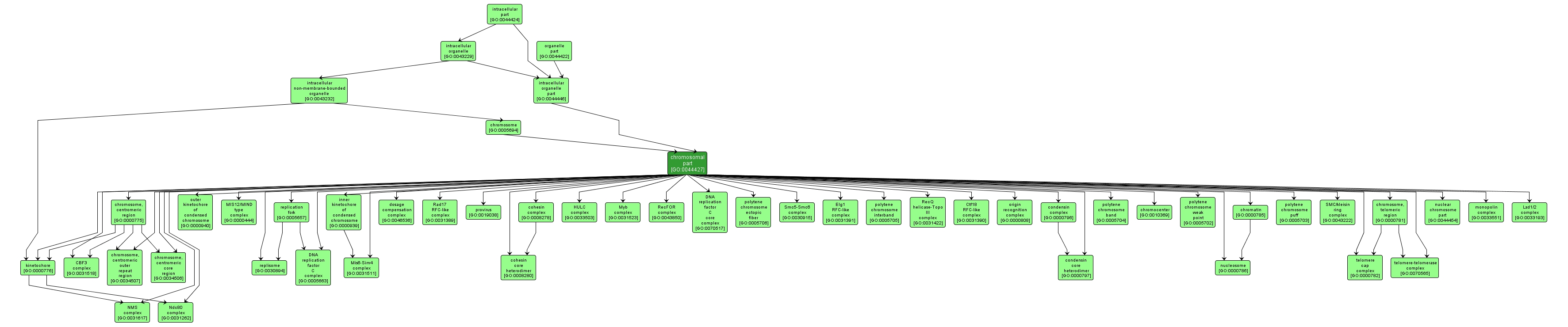
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
chromosomal part |
| Acc: |
GO:0044427 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
Any constituent part of a chromosome, a structure composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins (e.g. histones) that carries hereditary information. |
Synonyms:
- chromosomal component
- chromosome component
- chromosome part
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|