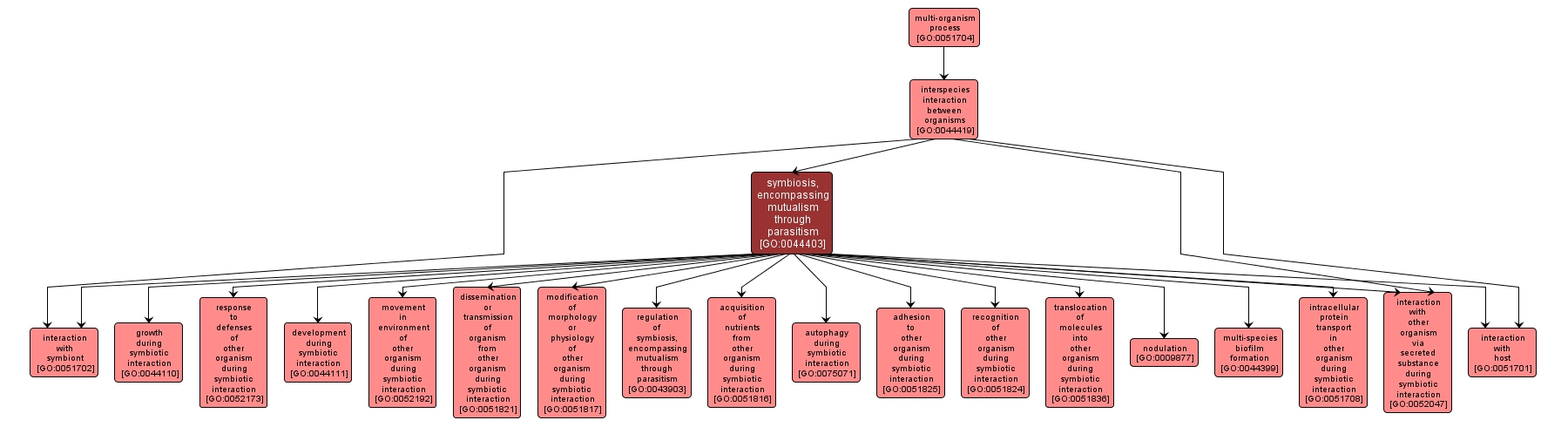
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
symbiosis, encompassing mutualism through parasitism |
| Acc: |
GO:0044403 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
An interaction between two organisms living together in more or less intimate association. The term host is usually used for the larger (macro) of the two members of a symbiosis. The smaller (micro) member is called the symbiont organism. Microscopic symbionts are often referred to as endosymbionts. The various forms of symbiosis include parasitism, in which the association is disadvantageous or destructive to one of the organisms; mutualism, in which the association is advantageous, or often necessary to one or both and not harmful to either; and commensalism, in which one member of the association benefits while the other is not affected. However, mutualism, parasitism, and commensalism are often not discrete categories of interactions and should rather be perceived as a continuum of interaction ranging from parasitism to mutualism. In fact, the direction of a symbiotic interaction can change during the lifetime of the symbionts due to developmental changes as well as changes in the biotic/abiotic environment in which the interaction occurs. |
Synonyms:
- host-pathogen interaction
- symbiotic interaction between organisms
- symbiosis
- symbiotic interaction between host and organism
- GO:0043298
- symbiotic interaction with other non-host organism
- symbiotic interaction
- GO:0044404
- symbiotic interaction between species
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|