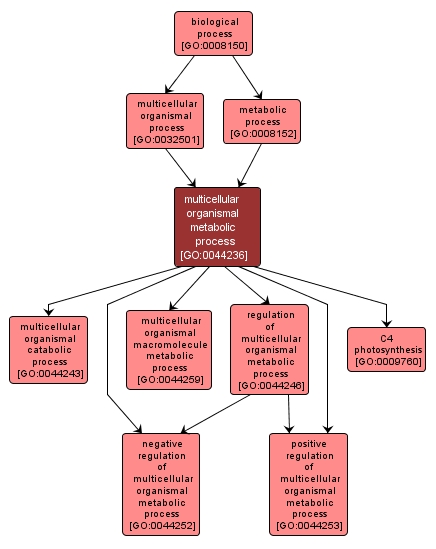
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
multicellular organismal metabolic process |
| Acc: |
GO:0044236 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The chemical reactions and pathways in multicellular organisms that occur at the tissue, organ, or organismal level. These processes, unlike cellular metabolism, can include transport of substances between cells when that transport is required. |
Synonyms:
- multicellular organismal metabolism
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|