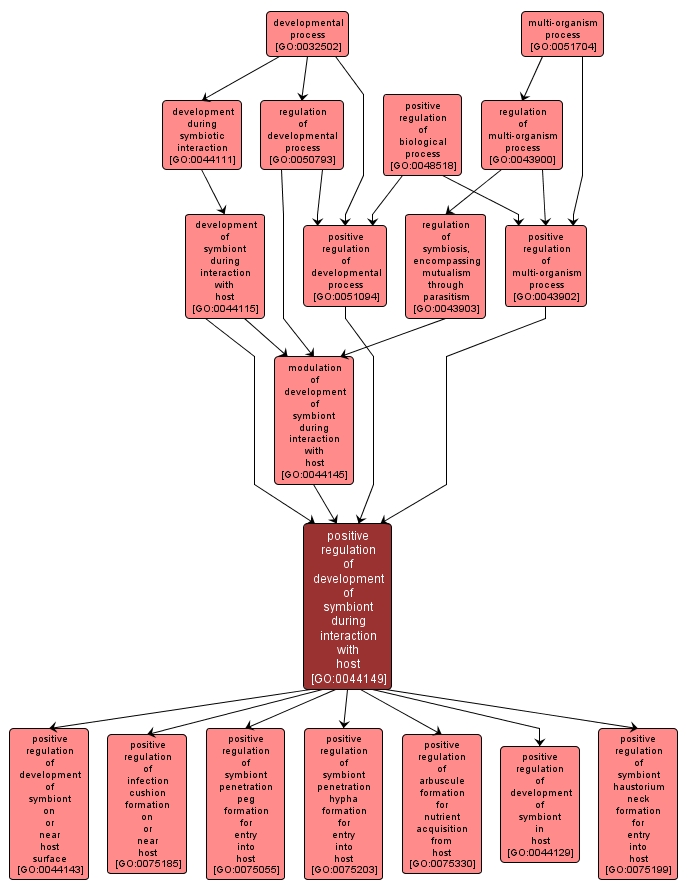
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
positive regulation of development of symbiont during interaction with host |
| Acc: |
GO:0044149 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the progression of an organism from an initial condition to a later condition, occurring in, on or near the exterior of its host organism. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|