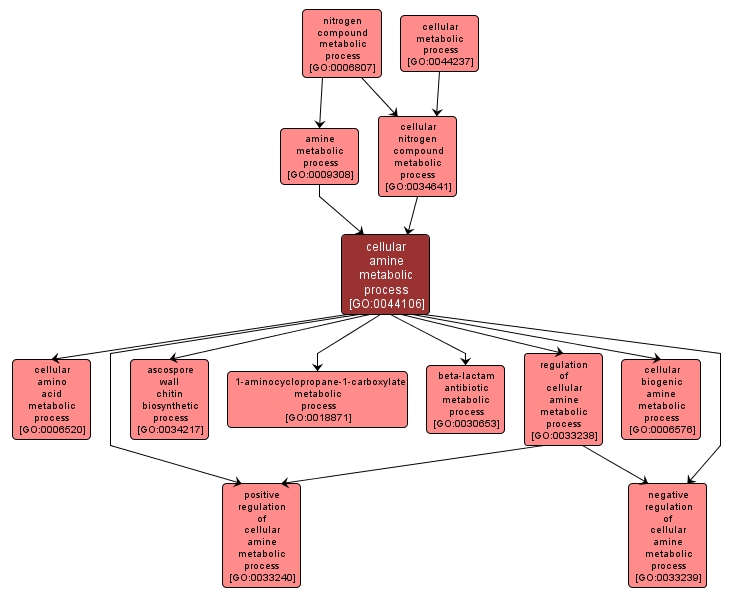
| Desc: |
The chemical reactions and pathways involving any organic compound that is weakly basic in character and contains an amino or a substituted amino group, as carried out by individual cells. Amines are called primary, secondary, or tertiary according to whether one, two, or three carbon atoms are attached to the nitrogen atom. |