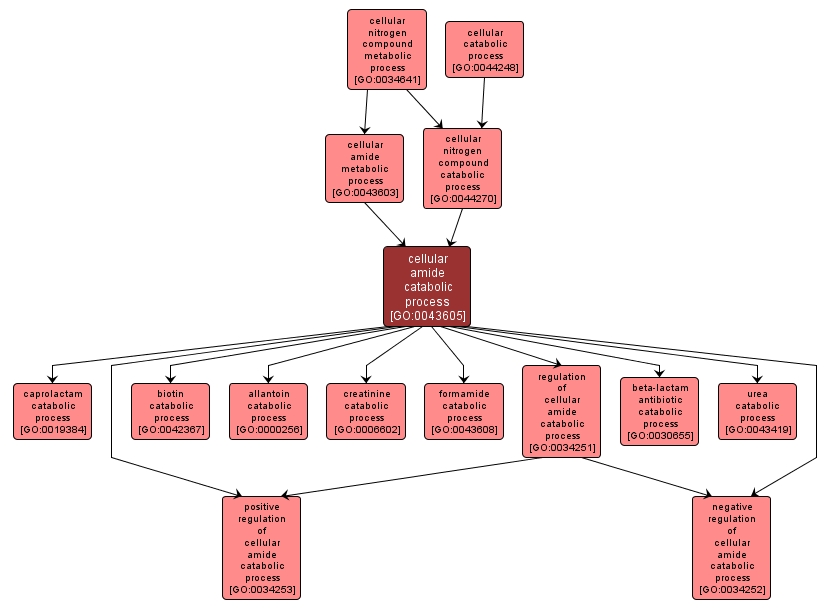
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
cellular amide catabolic process |
| Acc: |
GO:0043605 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of an amide, any derivative of an oxoacid in which an acidic hydroxy group has been replaced by an amino or substituted amino group. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|